DML Update
The DML Update (Data Manipulation Language) feature allows you to bulk update Salesforce records using a simple SQL-like syntax. This powerful feature enables you to modify field values across multiple records in a single operation, with support for formulas, field references, and various data types.
This is similar to DML statements that you might have used in RDBMS systems like Oracle or PostgreSQL.
Usage
Step 1: Write Your DML Statement
In the Query Editor, write your UPDATE statement following the syntax described below. See the Examples section below for guidance.
Make sure you always include the appropriate MAX clause number as well as any necessary WHERE conditions to avoid updating more records than intended.
Step 2: Execute the Statement
Select the DML text to be executed and click on the Execute button or use the keyboard shortcut Cmd+Enter (Mac)
or Ctrl+Enter (Windows).
Step 3: Review Confirmation Dialog
-
DML Update operations cannot be undone unless you have a backup. Review the information shown in the confirmation dialog carefully before executing the operation. Like they say, "measure twice, cut once."
-
App will only update the records if there are actual changes. If the new value is the same as the existing value, the record will be skipped and not counted as an updated record.
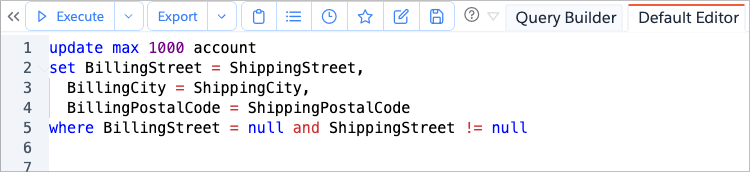
Brobench will validate your DML statement and show a confirmation dialog with:
- Number of records that will be updated
- The Salesforce object being updated
- Connection details where the update will be performed
- Generated SOQL query used to find matching records
- Ability to specify Save Options
Step 4: Configure Save Options
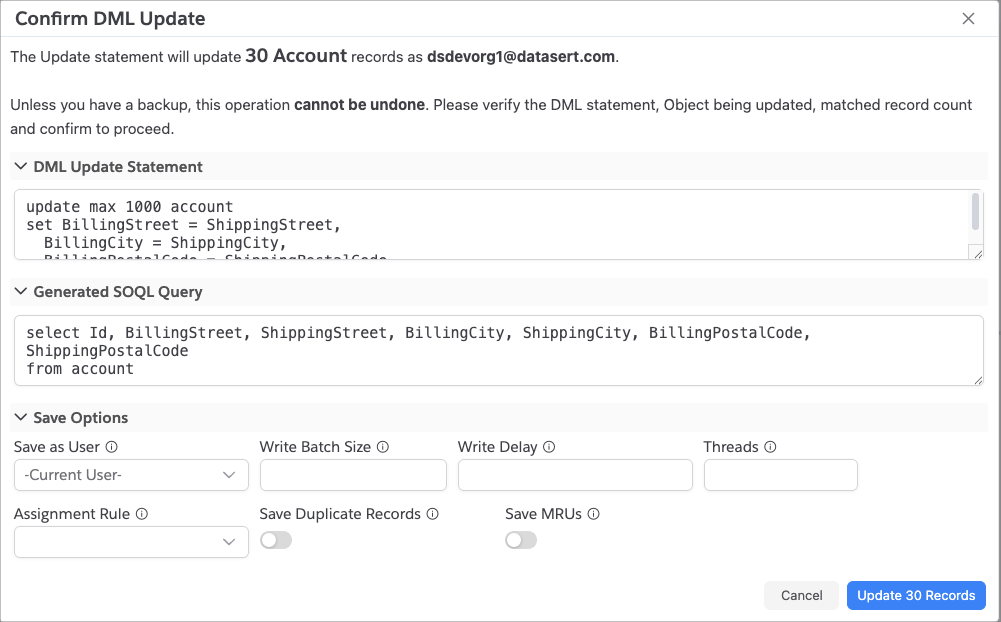
Expand the "Save Options" section in the confirmation dialog to configure:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Save as User | If you want to use different connection to perform updates, select that connection. Note that app will show only the Connection whose Sfdc Org Id matches current connection's | |
| Write Batch Size | 200 | Number of records per API call |
| Write Delay | - | Delay in milliseconds to wait before saving each batch of records |
| Threads | 1 | Number of parallel processing threads |
| Assignment Rule | - | Assignment rule for Accounts, Cases, or Leads |
| Save Duplicate Records | If there are any dedupe rules configure for the Object being updated, enable this will override the error and saves the changes. | |
| Save MRUs | Add updated records to Most Recently Used list |
Step 5: Execute Update
Click the Update X Records button to proceed.
Step 6: Monitor the Progress
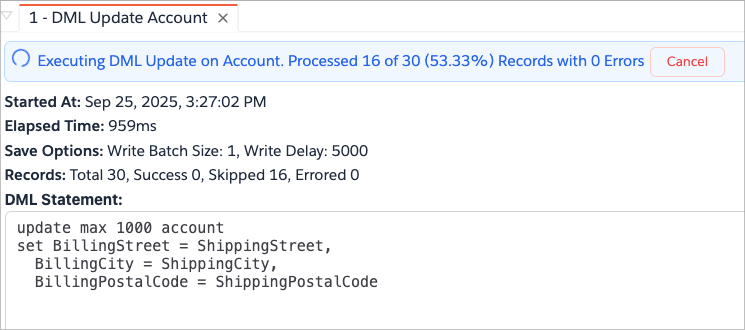
Brobench will open a new tab and show you the progress of the update operation in real-time.
Do NOT close the Brobench window until the process is complete. Closing the window will abort the operation and may leave your data in an inconsistent state.
Step 7: Cancel the Operation
If you would like to stop the operation before it completes, click the Cancel button. Note that records already
processed will not be reverted. App will ask you to confirm the cancellation and upon confirmation, will stop processing
any further records.
Step 8: Review Results
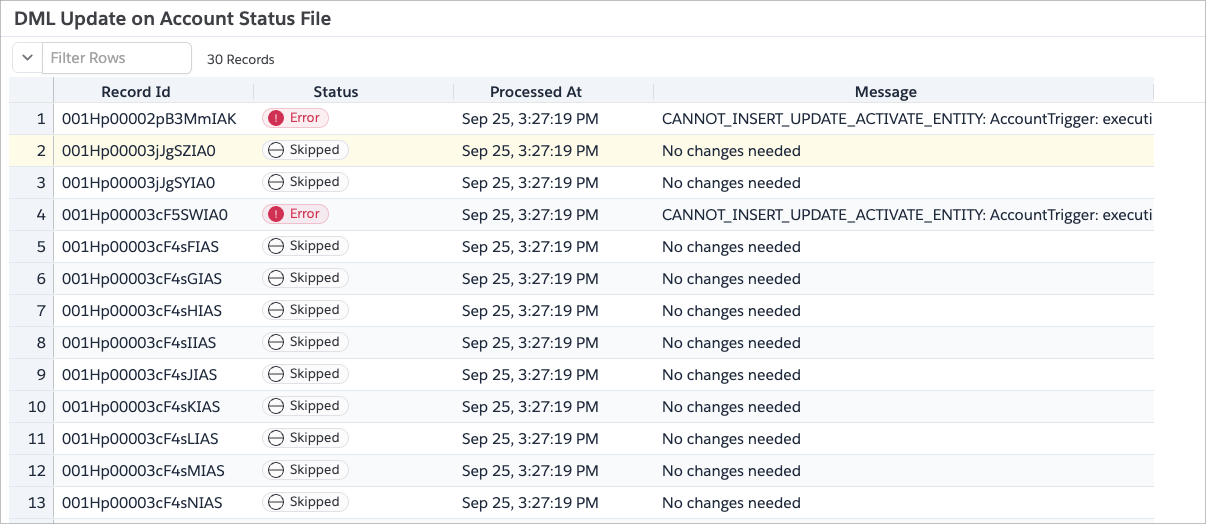
Once the operation is complete, Brobench will show you the results with statistics and a status file.
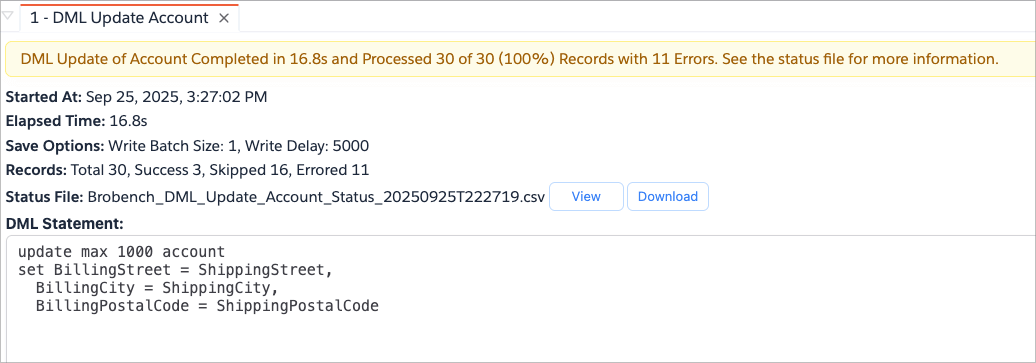
Click on the View status file button to see detailed status for each processed record. It shows the detailed status of
each record. You can also click on the Download button to download the status file as a CSV.
App will only update the records if there are actual changes. If the new value is the same as the existing value, the
record will be skipped and not counted as an updated record. For such records, the status will be set to Skipped
DML Update Statement Syntax
DML Update statements follow this syntax pattern:
UPDATE [MAX <max_records>] <SObject>
[WITH <field1>, <field2>, ...]
SET <field1> = <value1>, <field2> = <value2>, ...
[WHERE <conditions>]
[ORDER BY <field> ASC|DESC]
[LIMIT <number>]
[OFFSET <number>]
- The optional
MAXclause acts as a safety mechanism to prevent accidentally updating too many records. If you specify that clause with a count, then the app will error the operation if the query matches more records than that count. - The
WITHclause is required when using formula values and specifies which fields should be available for formula evaluation.
All the clauses in the DML statements are straightforward except for SET clause that needs some explanation.
- You can set multiple fields in the
SETclause separated by commas. - Each field can be set to a static value, a field reference, or a formula.
- String values should be enclosed in single quotes (
'). - Numeric values can be specified directly without quotes.
- Date values should be in
YYYY-MM-DDformat and not enclosed with quotes - DateTime values should be in
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZformat and not enclosed with quotes - Boolean values should be specified as
trueorfalsewithout quotes - To set a field to
NULL, use the keywordNULLwithout quotes - When using formula values, enclose the expression in double quotes (
") and ensure that all fields referenced in the formulas are included in theWITHclause
Update Examples
With MAX Clause
UPDATE MAX 100 Account
SET BillingCity = 'San Francisco', BillingState = 'CA'
WHERE BillingCountry = 'United States'
Static Values
String Value
UPDATE Account
SET BillingCity = 'San Francisco', BillingState = 'CA'
WHERE BillingCountry = 'United States'
Number Value
UPDATE Account
SET AnnualRevenue = 5000000, NumberOfEmployees = 100
WHERE Industry = 'Technology' AND Type__c = 'Customer'
Percentage Value
UPDATE Account
SET Discount_Percentage = 0.25
WHERE AnnualRevenue > 1000000
Date Value
UPDATE Account
SET Sync_Date__c = 2024-12-31
WHERE CreatedDate >= LAST_N_DAYS:30
Date Value
UPDATE Account
SET Approval_Time__c = 2025-09-25-00:00:00Z
WHERE IsApproved__c = true
Boolean Value
UPDATE Account
SET Is_Synced__c = false
WHERE CreatedDate >= LAST_N_DAYS:30
Null Value
UPDATE Account
SET Sync_Error__c = null
WHERE Sync_Status__c = 'Success'
Field Reference Value
UPDATE MAX 50 Contact
SET MailingStreet = BillingStreet,
MailingCity = BillingCity,
MailingState = BillingState
WHERE Account.Type = 'Customer'
Parent Field Reference Value
UPDATE MAX 50 Contact
SET MailingStreet = Parent.BillingStreet,
MailingCity = Parent.BillingCity,
MailingState = Parent.BillingState
WHERE Account.Type = 'Customer'
Formula Values
EnterpriseOne of the most powerful features of DML Update is the ability to use formulas to calculate new field values. Formulas are enclosed in double quotes and can reference any field specified in the WITH clause.
When using formula values in your UPDATE statement:
- The
WITHclause is required and must include all fields referenced in your formulas - If a field referenced in a formula is not listed in the WITH clause, the formula evaluation will be incorrect
- Formula syntax follows the Brobench Formula Engine rules
UPDATE Account
WITH BillingStreet, ShippingStreet, Name
SET BillingStreet = "upper_case(first_not_blank(BillingStreet, ShippingStreet))",
Name = "proper_case(Name)"
WHERE BillingCountry = 'United States'
String Manipulation:
UPDATE MAX 50 Contact
WITH FirstName, LastName, Email
SET Email = "lower_case(FirstName + '.' + LastName + '@company.com')"
WHERE Email = NULL
Numeric Calculations:
UPDATE Opportunity
WITH Amount, Probability
SET Amount = "Amount * (Probability / 100)"
WHERE StageName = 'Negotiation'
Date Operations:
UPDATE MAX 25 Case
WITH CreatedDate
SET FollowUpDate__c = "add_days(CreatedDate, 7)"
WHERE Status = 'New'
Advanced Features
Conditional Updates with Complex WHERE Clauses
UPDATE MAX 500 Opportunity
SET NextStep = 'Follow up with decision maker'
WHERE StageName IN ('Qualification', 'Needs Analysis')
AND Amount > 10000
AND CloseDate <= NEXT_30_DAYS
Using Relationship Fields
UPDATE Contact
WITH Account.BillingCity, Account.BillingState
SET MailingCity = "Account.BillingCity",
MailingState = "Account.BillingState"
WHERE Account.Type = 'Partner'
Boolean and Picklist Updates
UPDATE MAX 50 Lead
SET IsConverted = true,
Status = 'Qualified',
Rating = 'Hot'
WHERE Score__c >= 75
Runtime Errors
If errors occur during execution, they will be shown in the status file with specific error messages for each failed record. Common issues include:
- Validation Rule Failures: Record doesn't meet custom validation rules
- Required Field Missing: Required fields are not populated
- Field-Level Security: User doesn't have edit access to certain fields
- Duplicate Rules: Updates would create duplicate records
Best Practices
1. Start Small
Begin with a small MAX value to test your logic before processing large numbers of records.
-- Test with small batch first
UPDATE MAX 5 Account SET Industry = 'Technology' WHERE Name LIKE 'Tech%'
-- Then scale up after verification
UPDATE MAX 500 Account SET Industry = 'Technology' WHERE Name LIKE 'Tech%'
2. Use Specific WHERE Clauses
Always include precise WHERE clauses to avoid updating unintended records.
3. Leverage ORDER BY for Predictable Processing
UPDATE Case
SET Priority = 'High'
WHERE Status = 'New'
ORDER BY CreatedDate ASC
4. Monitor Resource Usage
For large updates, consider adjusting save options:
- Lower batch sizes if hitting governor limits
- Add delays between batches to reduce system load
- Use multiple threads carefully to avoid lock contention
5. Backup Critical Data
Always back up important data before performing bulk updates, especially when using formulas or complex logic.
Related Features
- DML Delete: Delete records in bulk
- DML Undelete: Restore deleted records
- Edit Data: Interactive record editing in data grids
- Export Records: Export query results
- Brobench Formulas: Formula syntax and functions